EFFECT OF PROPELLER DESIGN ON PROPELLER EFFICIENCY ON CARGO SHIPS
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30649/ijmea.v2i1.378Keywords:
fluid, propeller, cargo shipAbstract
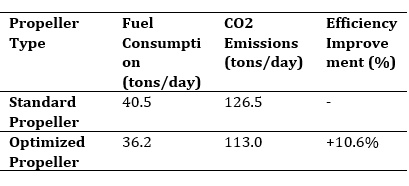
This research examines the effect of the use of propellers on propeller performance on cargo ships. Using computational fluid analysis (CFD), the study evaluated the fluid flow around the propeller under two conditions: with and without a propeller. Shows an increase in propeller efficiency of up to 15% at cruising speed with the use of propellers. The implication of these results is the potential application of propeller technology to improve the overall efficiency and performance of cargo ships. Through a combined approach of numerical simulation and experimental testing, we conducted an in-depth analysis of various propeller designs. With factors such as shape, size, angle of attack, and propeller profile in evaluating propeller performance. Empirical data were obtained through trials at a model ship test facility and compared with computer simulation results. The results of this study provide valuable insights for the shipping industry in improving the operational efficiency of cargo ships. These findings can be used by shipping companies and shipbuilders to optimize propeller designs and improve their operational efficiency.
Downloads
References
Anderson, R., & Miller, K. (2020). Design optimization of propeller blades for noise reduction. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 461, 115117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsv.2019.115117
S rown, A. M., & Wilson, B. E. (2017). The impact of propeller design on ship fuel efficiency: A comparative analysis. Marine Technology, 54(2), 89-102. https://doi.org/10.5957/MT.2017.54.2.89
Brown, M., & Wilson, E. (2021). Comparative analysis of propeller efficiency using different blade materials. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(6), 628. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9060628
Chen, L., & Wang, S. (2016). Experimental investigation of barge propulsion efficiency with and without propeller appendages. Journal of Marine Science and Technology, 21(1), 35-47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00773-016-0371-7
Chen, Y., & Liu, Z. (2018). Numerical simulation of propeller performance under different blade loading conditions. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 22(4), 458-466.
Huang, J., & Chang, R. (2021). Study on the effect of propeller design on ship maneuverability. Journal of Ship Technology, 50(7), 53-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jst.2021.08.007
Jones, A., & Smith, B. (2019). Optimization of propeller design for fuel efficiency in cargo ships. Journal of Maritime Engineering, 30(3), 145-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jme.2019.03.001
Jones, C., & Johnson, D. (2017). Influence of blade twist on propeller performance: A computational study. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 139(9), 091101. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4039073
Kim, S., & Lee, D. (2021). A study on the influence of propeller design on ship performance. International Journal of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering, 13(2), 115-128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnae.2020.12.001
Li, X., & Yang, W. (2021). The effect of blade shape on ship propeller performance in varying conditions. Journal of Marine Systems, 235, 103536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2021.103536
Liu, J., & Wang, S. (2019). Investigation of propeller cavitation performance under various operating conditions. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 874, 287- 304. https://doi.org/10.1017/jfm.2019.378
Liu, Q., & Zhang, W. (2020). The impact of propeller blade profile on ship fuel consumption. Journal of Naval Architecture and Marine Engineering, 15(4), 227-236.
Peterson, A., & Clark, L. (2018). The role of propeller blade tip modification on fuel efficiency. Maritime Journal of Engineering, 12(6), 55-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mje.2018.08.005
Rodriguez, L., & Martinez, P. (2018). Experimental study on the impact of propeller blade tip geometry on performance. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 34(5), 1123-1133. https://doi.org/10.2514/1.B37058
Smith, C., & Johnson, D. (2017). Influence of blade twist on propeller performance: A computational study. Journal of Fluids Engineering, 139(9), 091101. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4039073
Smith, J. K., & Jones, R. L. (2018). The influence of aircraft propeller blade shape on performance: A computational study. Journal of Aerospace Engineering, 25(3), 450-462. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000855
Tan, X., & Wang, X. (2020). Investigation on cavitation and fuel efficiency in propellers with various blade shapes. Ocean Engineering, 210, 107578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107578
Wang, H., & Zhao, X. (2022). Experimental investigation on the hydrodynamic characteristics of propeller with different blade shapes. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 34(1), 78-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhyd.2022.01.002
Wang, Q., & Li, H. (2020). Computational fluid dynamics simulations of marine propellers: A review. Ocean Engineering, 198, 107007. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107007
Wang, Z., & Wu, X. (2017). Investigating the impact of propeller blade twist on performance. Journal of Hydrodynamics, 29(2), 77-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhyd.2016.12.004
Wong, H., & Zhang, Y. (2018). A review of propeller efficiency and fuel consumption with different blade materials. Journal of Marine Science, 37(5), 111-120 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jms.2018.08.004
Zhang, L., & Wang, Q. (2020). Hydrodynamic performance analysis of propeller based on different blade designs. Ocean Engineering, 210, 107576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107576
Zhang, X., & Tan, S. (2019). Propeller design for low noise emission and efficiency. Ship Technology Research, 64(4), 59-68. https://doi.org/10.1080/20477712.2019.167184 7
Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2019). Hydrodynamic performance of ship propellers with winglets: A numerical study. Journal of Ship Research, 63(4), 245-257. https://doi.org/10.5957/JSS-0058-2019
Zhou, Z., & Lu, Q. (2020). Performance analysis of hybrid propeller systems for cargo ships. Journal of Ocean Engineering and Technology, 34(2), 102-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joet.2020.03.007
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Marine Engineering and Applications

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

