ANALYSIS OF PASSENGER EVACUATION ON FERRY KMP TRISNA DWITYA USING PATHFINDER
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30649/ijmea.v2i1.382Keywords:
KNKT, ship accident, IMO, evacuation, pathfinderAbstract
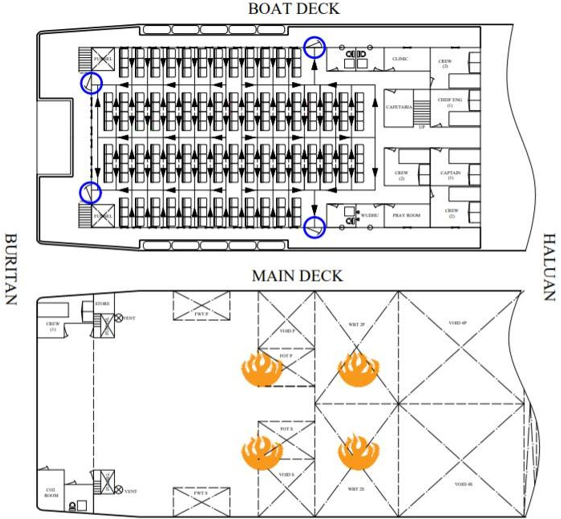
The use of ships as a transportation is growing rapidly, of course, this is also related to transportation safety related including ship accidents. The National Transportation Accident Commission (KNKT) recorded 86 accidents in the sea transportation sector from 2010 to 2019. In 2018, the KMP Trisna Dwitya ferry ran aground, which resulted in 28 passengers having to be evacuated. Safety on ships must be optimized by minimizing casualties. The determining factor in evacuation is the time it takes for passengers to get out of the waiting room on the ship. Hence, it is necessary to calculate the time for the evacuation process. The purpose of this study is to obtain results in the form of evacuation time during a fire and evaluate the simulation of passenger evacuation in the fastest time. The method used is modeling and simulation, where modeling is used to simulate and analyze the time required for evacuation with the Pathfinder software. The results of the analysis and simulation yielded 3 different scenarios. Scenario 1: When the fire point is on the main deck where the motorized vehicle with evacuation time reaches 20 minutes 21 seconds. Scenario 2, when the fire point is in the left side engine room, reaches 20 minutes 57 seconds. Scenario 3, when the fire point is in the right-side engine room, the time obtained is 21 minutes 1 second. So that the 3 scenarios have met the requirements of the IMO, which is less than 60 minutes during the evacuation process on a passenger ship.
Downloads
References
Nempung, T. dan Jusna, J. Peranan Transportasi Laut Dalam Menunjang Arus Barang Dan Orang Di Kecamatan Maligano Kabupaten Muna. Jurnal Ekonomi. Vol.1, No. 1 (2016) pp.189–200.
Lopez pineiro, A., Arribas F.P., Donoso, R. and Torres, R. Simulation Of Passengers Movement On Ship Emergencies. Tools For Imo Regulations Fulfilment. Journal of Maritime Research. Vol. II No.1 (2005) pp. 105–125.
Muhammad, A.H. and Paroka, D. Lokasi Kritis Jalur Evakuasi Penumpang Kapal Penyeberangan Antar Pulau Dengan Metode Pergerakan Simultan. Vol. 15 No. 2 (2015) pp. 125–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26593/jtrans.v15i2.1730.%25 p
Lee, D., Park, J.H. and Kim, H. 2004. A Study on Experiment of Human Behavior for Evacuation Simulation. Ocean Engineering. Vol. 31, Issue 8-9 (2004) pp. 931-941. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oceaneng.2003.12.003
CNN Indonesia. KMP Trisna Dwitya Kandas, 28 Penumpang Dievakuasi. 2018. https://www.cnnindonesia.com/nasional/201807 15133552-20-314176/kmp-trisna-dwitya- kandas-28-penumpang-dievakuasi.
Matafi, S.N, Dien, H.V. dan Pangalila, F.P.T. Simulasi Pengaruh Trim terhadap Stabilitas Kapal Pukat Cincin. Jurnal Ilmu dan Teknologi Perikanan Tangkap. Vol.2 Edisis Khusus (2015) pp. 13-18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.35800/jitpt.2.0.2015.6966
Mulyatno I.M., Manik P., dan Addawiyah S.A. Analisa Lifeboat Placement Effectiveness terhadap Proses Evakuasi Kapal Penumpang Menggunakan Metode Agent Based Modelling Simulation. Jurnal Rekayasa Mesin Vol. 14, No.2 (2023) pp. 571-586. DOI: 10.21776/jrm.v14i2.1348
Farrand J., Mulyatno I.M., Adietya B.A., Analisa Evakuasi Penumpang Dengan Metode Pendekatan Simulasi Berdasarkan Aturan IMO Msc.1/Circ.1533 Pada Kapal Penyebrangan Penumpang 5000 GT. Jurnal Teknik Perkapalan Vol. 12, No. 2 (2024) pp. 1-10.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 International Journal of Marine Engineering and Applications

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.

